Network Engineer Interview Preparation Classes
Join our Network Engineer Interview Preparation Classes and boost your confidence with expert guidance. Gain in-depth knowledge of networking concepts, hands-on practice, and tips for tackling technical questions. Perfect for freshers and professionals!
1. What is a network?
A network is a collection of interconnected devices, such as computers and servers that communicate and share resources with each other. Hence, we can also say that a network is a collection of interconnected devices, such as computers, servers, switches, routers, and other hardware, that communicate and share resources. These devices are linked using communication protocols over various mediums like cables, fiber optics, or wireless signals.
2. What is a LAN?
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that covers a small geographical area, typically within a single building or campus. Hence, we can also say that a LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, school, or campus. It enables the sharing of resources like files, printers, and internet access among connected devices.
3. What is a WAN?
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network that covers a larger geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs across different locations. Hence, we can also say that a WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network that connects devices and networks over large geographical areas, such as cities, countries, or even continents. It is used to link smaller networks, like LANs or MANs, to enable communication and resource sharing across vast distances.
4. What is an IP address?
An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. It is used to identify and locate devices on the network. An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. It allows devices to locate and communicate with one another over the internet or a local network. Think of it as a digital address for your device. Hence, to understand IP address in more details join us for CCNA Training.
5. What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and provides approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses and provides an almost infinite number of unique addresses. IPv4 and IPv6, the two main versions of the Internet Protocol.
Address Format and Size
- IPv4:
- 32-bit address.
- Represented in decimal, separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- Can support approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses.
- IPv6:
- 128-bit address.
- Represented in hexadecimal, separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
- Can support about 3.4×10383.4 \times 10^{38} unique addresses, enough for massive future scalability.
6. What is a subnet mask?
A subnet mask is a 32-bit number used to divide an IP address into network and host portions. It helps determine which part of the IP address represents the network and which part represents the host. A subnet mask is a 32-bit number used in networking to divide an IP address into two parts: the network portion and the host portion. It helps determine which part of the IP address identifies the network and which part identifies the specific device (host) within that network. Hence, to understand subnetting in more details join us for best CCNA Training Course.
7. What is a default gateway?
A default gateway is the IP address of the router or gateway device that connects a local network to other networks or the internet. Hence, we can say that a default gateway is a network device, typically a router, that serves as an access point for devices within a network to communicate with devices on another network, such as the internet. It acts as a bridge between a local network (LAN) and external networks.
8. What is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is a system that translates domain names into IP addresses. It allows users to access websites using human-readable names instead of numeric IP addresses. Hence, we can say that DNS (Domain Name System) is a system that translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses (like 192.0.2.1) so devices can locate and communicate with each other over the internet. It acts like a phonebook for the internet, making it easier for users to access websites and services without remembering numerical IP addresses. Hence, to understand DNS in better way join our CCNA Certification Course.
9. What is DHCP?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network. Hence, we can also say that a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network management protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other configuration settings (such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server) to devices on a network. This eliminates the need for manual configuration, making it easier to manage large networks.
10. What is a firewall?
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Hence, a firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet, to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyber threats.
11. What is NAT?
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a technique used to translate private IP addresses used within a local network into public IP addresses used on the internet.
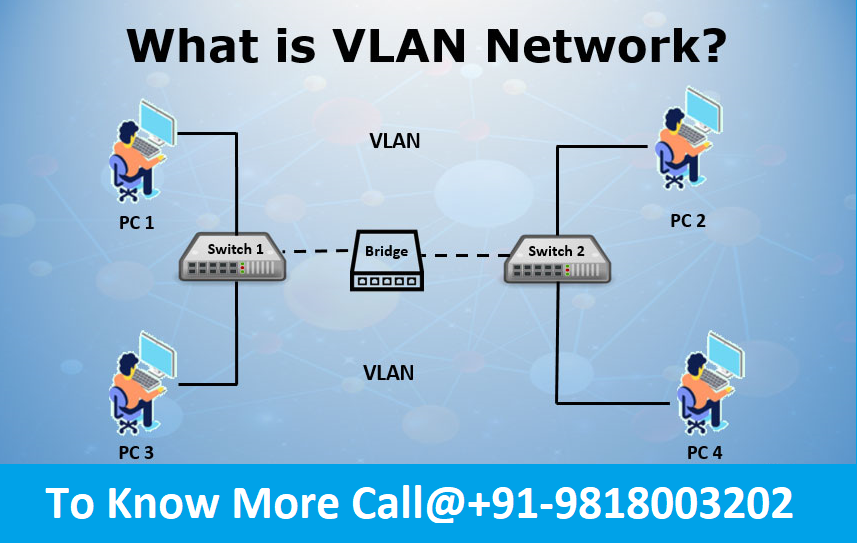
12. What is VLAN?
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical grouping of devices within a network. It allows the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical network. A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical grouping of devices on a network that allows them to communicate as if they were on the same physical network, even if they are located on different physical networks. VLANs improve network performance, security, and manageability by segmenting traffic and isolating devices based on function, department, or other criteria.
13. What is the difference between a hub, a switch, and a router?
A hub is a simple networking device that broadcasts data to all connected devices. A switch is an intelligent device that forwards data only to the intended recipient. A router is a device that connects different networks and forwards data packets between them.
14. What is OSPF?
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a routing protocol used to determine the best path for data to travel in an IP network.
15. What is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a secure connection that allows users to access a private network over a public network, such as the internet.
16. What is a MAC address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to the network interface card of a device. It operates at the data link layer of the OSI model.
17. What is the OSI model?
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that describes the different layers involved in network communication. It consists of seven layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
18. What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol that guarantees reliable data delivery, while UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that does not provide guaranteed delivery.
19. What is latency?
Latency is the time delay experienced in a network communication. It is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination.
20. What is a proxy server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a client and the internet. It forwards client requests and retrieves responses from the internet on behalf of the client.
21. What is the purpose of ARP?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to map an IP address to a MAC address on a local network.
22. What is a DNS server?
A DNS server is a server that stores DNS records and provides name resolution services by translating domain names into IP addresses.
23. What is ICMP?
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network protocol used for diagnostic and error reporting purposes. It is commonly used for ping and traceroute operations.
24. What is a proxy ARP?
Proxy ARP is a technique used by a router to respond to ARP requests on behalf of hosts on a different network segment.
25. What is a DNS cache?
A DNS cache is a temporary storage of recently resolved domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. It helps improve DNS lookup performance by reducing the need for repeated lookups.
26. What is the purpose of a MAC table?
A MAC table is used by a switch to keep track of MAC addresses and their associated port locations. It helps the switch determine where to forward network traffic.
27. What is a VLAN trunk?
A VLAN trunk is a network link that carries multiple VLANs. It allows multiple VLANs to be transmitted over a single physical link.
28. What is the purpose of NAT traversal?
NAT traversal is a technique used to establish and maintain IPsec VPN connections through NAT devices, which often cause issues with VPN traffic.
29. What is STP?
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a network protocol that prevents loops in Ethernet networks by blocking redundant paths and establishing a loop-free logical topology.
30. What is the purpose of QoS?
QoS (Quality of Service) is a set of techniques used to prioritize and manage network traffic to ensure optimal performance for critical applications.
31. What is the difference between half-duplex and full-duplex communication?
In half-duplex communication, data can be transmitted in both directions, but not simultaneously. In full-duplex communication, data can be transmitted simultaneously in both directions.
32. What is a MAC flooding attack?
A MAC flooding attack is a network security attack where an attacker floods a switch’s MAC table with fake MAC addresses, causing it to enter into a fail-open mode and potentially allowing unauthorized access to the network.
33. What is the purpose of BGP?
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is an exterior gateway protocol used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the internet.
34. What is the purpose of a network mask?
A network mask is used to determine the network portion of an IP address by performing a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the network mask.
35. What is a network loop?
A network loop occurs when there is a redundant path or multiple connections between network switches, causing broadcast or multicast traffic to circulate indefinitely.
36. What is PoE?
PoE (Power over Ethernet) is a technology that allows network devices to receive power and data over a single Ethernet cable.
37. What is a MAC spoofing attack?
A MAC spoofing attack is a network security attack where an attacker impersonates the MAC address of another device to gain unauthorized access or perform malicious activities on the network.
38. What is the purpose of a network gateway?
A network gateway is a device that connects networks with different network protocols or architectures. It acts as an entry or exit point for network traffic between networks.
39. What is a multicast address?
A multicast address is an IP address used to deliver data packets to a group of devices that have joined a multicast group. It allows efficient distribution of data to multiple recipients.
40. What is the purpose of NAT reflection?
NAT reflection is a technique used to enable devices on a local network to access resources using the public IP address of the network, even when they are within the same network.
41. What is VLAN tagging?
VLAN tagging is the process of adding additional information, such as a VLAN ID, to network frames. It allows switches to identify and handle frames belonging to different VLANs.
42. What is a network protocol?
A network protocol is a set of rules and conventions that govern how data is transmitted, received, and processed in a network. It ensures consistent and reliable communication between devices.
43. What is the purpose of a network proxy?
A network proxy acts as an intermediary between clients and servers, intercepting requests and responses to provide additional functionality, such as caching, filtering, or security services.
44. What is a DHCP relay agent?
A DHCP relay agent is a device that forwards DHCP messages between clients and DHCP servers in different network segments, allowing clients to obtain IP addresses and configuration information from DHCP servers located elsewhere.
45. What is the purpose of a network bridge?
A network bridge connects two or more network segments together at the data link layer, allowing devices in different segments to communicate as if they were on the same network.
46. What is a loopback address?
A loopback address is a special IP address, usually 127.0.0.1 that represents the local host or the device itself. It is commonly used for testing network connectivity on the local machine.
47. What is a network anomaly?
A network anomaly is any deviation from the expected or normal behavior in a network. It may indicate a security breach, performance issue, or other network problems.
48. What is the purpose of ARP poisoning?
ARP poisoning, also known as ARP spoofing, is a network attack where an attacker falsifies ARP messages to associate their MAC address with the IP address of another device. This allows the attacker to intercept or modify network traffic.
49. What is a network switch fabric?
A network switch fabric is the internal architecture or design of a switch that determines how data is forwarded between ports and processed within the switch.
50. What is the purpose of a network load balancer?
A network load balancer distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources to ensure efficient utilization, high availability, and scalability.